BMI Calculator
BMI Calculator For Men Over 50
BMI calculator for men over 50 provides a useful starting point for health assessment, but its results must be interpreted with crucial age-related considerations in mind. While the standard formula weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared remains the same, the ideal healthy range can be less rigid, as some studies suggest a slightly higher BMI may correlate with better longevity in older adults. However, this does not negate the significant health risks associated with clinical obesity. More importantly, a standard BMI cannot distinguish between weight from muscle and weight from fat, making it a limited tool for aging men who may be losing muscle mass. Therefore, the calculated number should be viewed as one data point alongside metrics like waist circumference, strength, and overall physical function.
BMI Chart for Seniors
BMI chart for seniors, it’s crucial to understand that standard healthy ranges may require age-adjusted considerations for older adults. While a BMI of 18.5 to 24.9 is typically classified as normal, research suggests that a slightly higher range up to 27 may be associated with better health outcomes and longevity in the elderly population, as some reserve weight can protect against illness and frailty. However, this does not diminish the risks of obesity, and a BMI over 30 generally remains a health concern. For seniors, the focus should shift from weight alone to overall body composition, prioritizing muscle mass preservation and functional health over strict adherence to a traditional chart.

BMI Table for Adults
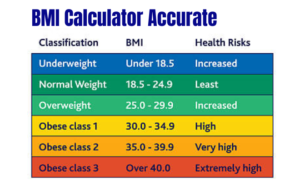
This standard reference table classifies body weight status based on Body Mass Index (BMI) for individuals aged 20 and above. It provides ranges that correspond to categories such as Underweight, Normal weight, Overweight, and various Obesity classes. It is important to note that this table is a general screening tool and does not account for individual factors like muscle mass, bone density, or body composition. Therefore, it should be used as a starting point for understanding health risks associated with weight. For a comprehensive health assessment, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional who can consider your unique circumstances. Use the calculator and table as guides, not as definitive diagnostic tools.
BMI Calculator FAQs
Find answers to common questions about Body Mass Index (BMI) and how to use our calculator
About BMI Calculation
BMI (Body Mass Index) is a measure of body fat based on height and weight that applies to adult men and women. It's calculated by dividing a person's weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters (kg/m²).
For imperial units, the formula is: (weight in pounds / (height in inches)²) x 703.
Our calculator automatically handles both metric and imperial units, so you don't need to do any conversions.
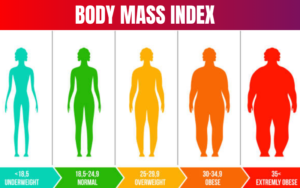
For adults, BMI is categorized as follows:
| BMI Range | Category |
|---|---|
| Below 18.5 | Underweight |
| 18.5 - 24.9 | Normal weight |
| 25.0 - 29.9 | Overweight |
| 30.0 and above | Obese |
Note: These categories are for adults aged 20 and older. BMI interpretation for children and teens is different.
Yes, BMI interpretation for children and teens is different from adults. Instead of fixed categories, children's BMI is compared to percentiles for their age and gender.
The categories for children are:
- Underweight: BMI below the 5th percentile
- Healthy weight: BMI between 5th and 85th percentile
- Overweight: BMI between 85th and 95th percentile
- Obese: BMI at or above the 95th percentile
Our calculator automatically adjusts interpretation based on the age you enter.
Using the Calculator
Our BMI calculator uses the standard formulas endorsed by health organizations worldwide, so the calculations are mathematically accurate.
However, it's important to understand that BMI is a screening tool, not a diagnostic one. It provides a general indication of whether you're at a healthy weight, but it doesn't account for factors like muscle mass, bone density, or body composition.
Tip: For a more comprehensive health assessment, consider additional measurements like waist circumference, body fat percentage, and consultation with a healthcare provider.
We ask for gender and age to provide the most accurate interpretation of your BMI result:
- Gender: While the BMI calculation is the same for men and women, the interpretation may vary slightly due to physiological differences in body composition.
- Age: BMI interpretation is different for children and adults. For children, we use age- and gender-specific percentiles rather than fixed categories.
Yes! Our calculator allows you to easily switch between metric (centimeters and kilograms) and imperial (inches and pounds) units.
Simply click the "Metric" or "Imperial" buttons at the top of the calculator. The units will automatically update, and you can enter your measurements in your preferred system.
Health & Limitations
While BMI is a useful screening tool, it has several limitations:
- Muscle vs. Fat: BMI doesn't distinguish between muscle and fat, so athletes with high muscle mass may have a high BMI but low body fat.
- Fat Distribution: It doesn't account for where fat is located on the body, which is important for health risks.
- Age Considerations: It may not be as accurate for older adults who have lost muscle mass.
- Ethnic Differences: Some ethnic groups may have different health risks at the same BMI.
- Pregnancy: BMI is not accurate during pregnancy.
Yes, BMI can be misleading for athletes and very muscular individuals. Since muscle is denser and weighs more than fat, these individuals may have a high BMI that classifies them as overweight or obese, even though they have low body fat and are in excellent health.
If you're an athlete or have a muscular build, consider additional assessments like body fat percentage measurements or waist-to-hip ratio for a more accurate health evaluation.
For most adults, checking your BMI every 3-6 months is sufficient unless you're actively trying to change your weight. For children, regular monitoring (every 6-12 months) is recommended as they grow.
Remember: Focus more on developing healthy habits (balanced diet, regular exercise) rather than frequent BMI checks. Your overall health is more important than a single number.
If your BMI falls outside the normal range:
- Don't panic: BMI is just one indicator of health.
- Consult a professional: Speak with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
- Focus on habits: Instead of quick fixes, work on sustainable lifestyle changes.
- Consider other factors: Look at your eating patterns, activity levels, sleep quality, and stress management.
Our calculator provides general guidance, but individual health needs vary. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.

Leave a Reply