BMI Calculator
Normal BMI
Maintaining a healthy BMI is a fundamental indicator of overall well-being and a key component of preventive health. Calculated from an individual’s height and weight, a BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 falls within the healthy range, suggesting a lower risk for weight-related health issues. This simple measurement helps assess whether one is underweight, at a normal weight, overweight, or obese. Striving for a healthy BMI through balanced nutrition and regular physical activity is crucial for long-term wellness. It significantly reduces the risk of developing chronic conditions such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. Ultimately, understanding and managing your BMI is a proactive step towards a healthier, more vibrant life.
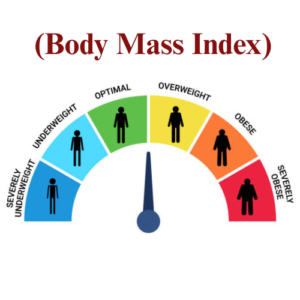
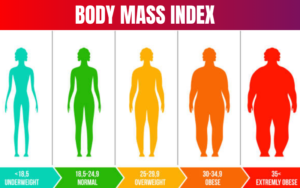
BMI Range refers to the categories used to interpret your Body Mass Index (BMI) value, helping determine whether your weight is underweight, normal, overweight, or obese. It is calculated by dividing your weight in kilograms by your height in meters squared (kg/m²). According to WHO and CDC standards, a BMI below 18.5 is considered underweight, 18.5–24.9 is normal, 25–29.9 is overweight, and 30 or above is obese. Understanding your BMI range is essential for assessing overall health and potential risk factors related to weight. It helps individuals maintain a healthy balance between diet, exercise, and lifestyle. Regularly tracking your BMI can guide better health choices and prevent long-term health issues.
BMI Calculator
BMI (Body Mass Index) Calculator is a simple tool that helps you measure your body fat based on your height and weight. It provides a quick way to determine whether you are underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. The BMI value is calculated by dividing your weight (in kilograms) by your height (in meters squared). BMI is an essential health indicator used worldwide by doctors and fitness experts. It helps you understand if your body weight is in a healthy range for your height, which can reduce the risk of diseases like diabetes, heart problems, and high blood pressure.
BMI Formula
The Formula:
BMI = weight (kg) / [height (m)]²
Example in Metric:
-
Weight: 65 kg
-
Height: 1.70 m
-
Calculation: 65 / (1.70 * 1.70) = 65 / 2.89 = 22.5
Alternative Formula (using pounds and inches):
BMI = [weight (lbs) / height (in)²] x 703
Example in Imperial:
-
Weight: 140 lbs
-
Height: 65 inches
-
Calculation: [140 / (65 * 65)] x 703 = [140 / 4225] x 703 = 0.0331 x 703 = 23.3
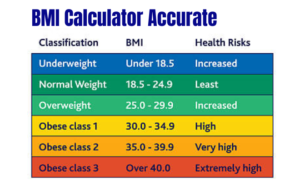
BMI Categories (World Health Organization):
-
Underweight: BMI less than 18.5
-
Normal Weight: BMI 18.5 – 24.9
-
Overweight: BMI 25 – 29.9
-
Obesity Class I: BMI 30 – 34.9
-
Obesity Class II: BMI 35 – 39.9
-
Obesity Class III: BMI 40 or greater
Cost-Effective Tool
BMI calculation is inexpensive and requires no special equipment. This makes it an ideal first-step screening tool in clinical settings and for personal health monitoring.
Muscle vs. Fat Misrepresentation
BMI doesn’t distinguish between muscle and fat. Athletes with high muscle mass may be classified as overweight or obese, while individuals with normal BMI may have high body fat percentages.
Limited Demographic Accuracy
BMI may not account for ethnic differences in body composition. It also doesn’t consider age, sex, or bone structure, which can affect the interpretation of results across different populations.
Fat Distribution Ignored
BMI doesn’t indicate where fat is stored in the body. Visceral fat around organs is more dangerous than subcutaneous fat, but BMI cannot make this important distinction.
Quick & Easy Assessment
BMI provides a simple and fast method to screen for weight categories that may lead to health problems. It requires only two measurements – height and weight – making it accessible for everyone.
Population Health Tracking
BMI is valuable for tracking weight trends in large populations. It helps public health officials identify obesity trends and allocate resources effectively for community health initiatives.
Why is BMI Important?
BMI is an essential health indicator used worldwide by doctors and fitness experts. It helps you understand if your body weight is in a healthy range for your height, which can reduce the risk of diseases like diabetes, heart problems, and high blood pressure.
BMI formula
The Body Mass Index (BMI) formula is a simple mathematical calculation used to estimate a person’s total body fat based on their weight and height.
The universal formula for calculating BMI is:
BMI = weight (kg) / height (m)²
For the imperial system (using pounds and inches), the formula is adjusted as:
BMI = (weight (lbs) / height (in)²) x 703
BMI For a General Health & Wellness
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used screening tool to categorize individuals based on their weight relative to their height. By simply entering your height and weight, our calculator provides a numerical value that places you in a standard weight status category, such as underweight, healthy weight, overweight, or obese. While it’s a useful starting point for assessing health risks associated with weight, it’s important to remember that BMI does not directly measure body fat percentage or account for factors like muscle mass, bone density, and overall body composition.
BMI For a Focusing on Health Risks and Medical Use
Healthcare professionals use Body Mass Index (BMI) as a quick, standardized method to identify potential weight-related health risks. A high BMI can be an indicator of increased susceptibility to conditions such as heart disease, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. Conversely, a low BMI may signal other health concerns, including nutritional deficiencies or a weakened immune system. It serves as an initial screening tool to prompt further discussion with a doctor about a comprehensive health plan.
Additional insights for what’s my BMI calculator
When to Use BMI
BMI is best used as a general screening tool rather than a diagnostic measure. For a complete health assessment, combine BMI with other measurements like waist circumference, body fat percentage, and blood tests.
Better Alternatives
For more accurate health assessments, consider waist-to-hip ratio, body fat percentage measurements (DEXA scan, BIA), or waist circumference. These provide better indicators of health risks related to body composition.
Risks Associated with Being Underweight
- A number of health hazards, such as decreased immunity, brittle bones, exhaustion, and nutritional shortages, can result from being underweight. A healthy weight must be maintained for general wellbeing.
- Health problems like low energy, weakened immunity, and an increased risk of bone and fertility problems can affect those who are underweight. A healthy diet and way of living are essential for healing.
- Being underweight raises the danger of severe health issues, vitamin shortages, and weak muscles. It’s not just about beauty.
- Your body may have trouble maintaining its health if it doesn’t get enough fat and nutrients. People who are underweight may feel exhausted, get sick more often, and recuperate more slowly.
Leave a Reply